Heart-Leaf Philodendron (Philodendron hederaceum): A Care Guide
This guide provides detailed instructions for growing the Heart-Leaf Philodendron (Philodendron hederaceum). It covers identification, distinguishing it from Pothos, care requirements like light and water, propagation methods, common cultivars, and toxicity information.
Section 1: Introduction
The Heart-Leaf Philodendron, Philodendron hederaceum , is among the most common houseplants, known for its heart-shaped leaves and trailing vines. It is often a first plant for new gardeners because it is tolerant and resilient. 1 According to horticultural sources, it is one of the most popular philodendrons sold today. 1

While easy to grow, P. hederaceum is a morphologically complex plant. When left to trail, it keeps its small, juvenile leaves. If given a surface to climb, it will develop much larger leaves, showing the growth habit of its wild ancestors. 1 This adaptability, along with its tolerance for a range of indoor conditions, makes it a popular houseplant. 2
| Botanical Profile of Philodendron hederaceum | |
|---|---|
| Accepted Scientific Name | Philodendron hederaceum (Jacq.) Schott 1 |
| Common Synonyms | Philodendron scandens , Philodendron oxycardium 1 |
| Common Names | Heart-Leaf Philodendron, Sweetheart Plant 2 |
| Family | Araceae (the Arum family) 1 |
| Native Range | Mexico, the Caribbean, Central and South America 1 |
| Plant Type | Evergreen vining perennial, hemiepiphyte 3 |
Section 2: Botanical Naming and History
The scientific name for the Heart-Leaf Philodendron has a long history of confusion. The plant is often sold under the names Philodendron scandens or Philodendron oxycardium , but its correct and accepted name is Philodendron hederaceum . 5
The plant was first described in 1760 as Arum hederaceum . In 1829, botanist Heinrich Wilhelm Schott reclassified it into the Philodendron genus, establishing the name Philodendron hederaceum . 5
P. hederaceum is a highly variable species. Its leaf size and shape change significantly as it matures from a juvenile plant into an adult vine, a process known as ontogeny. 8 In the past, this led botanists to mistakenly identify different growth stages as separate species, resulting in names like P. scandens and P. oxycardium . 5
Botanical nomenclature follows the principle that the first validly published name for a species is the accepted one. All other names for the same species are considered synonyms. 5 This is a standard scientific process for correcting historical errors.
Today, major botanical institutions like the Missouri Botanical Garden (MOBOT) and the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, list Philodendron hederaceum as the accepted scientific name, with P. scandens and P. oxycardium as synonyms. 1 This also applies to the popular velvety-leaved 'Micans', which is a naturally occurring form of P. hederaceum , not a distinct species. 7
Although synonyms like P. scandens are still common in the nursery trade, using the correct name, Philodendron hederaceum , reflects a more accurate understanding of the plant. 9
Section 3: Distinguishing from Pothos (Epipremnum aureum)
The Heart-Leaf Philodendron is often confused with Golden Pothos ( Epipremnum aureum ) due to their similar vining habit and heart-shaped leaves. 3 Both are in the Araceae family and have similar care needs, but they belong to different genera and have several distinct features for identification. 12
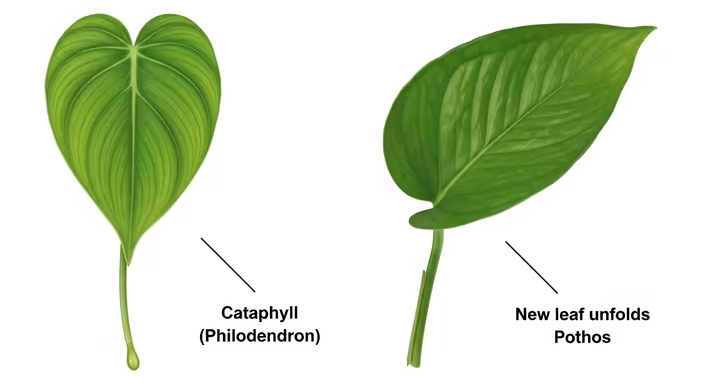
Observing the leaves, stems, and new growth reveals consistent differences between the two plants.
| Philodendron hederaceum vs. Epipremnum aureum (Pothos) - A Definitive Comparison | |
|---|---|
| Characteristic | Heart-Leaf Philodendron ( P. hederaceum ) |
| Leaf Shape & Tip | More symmetrical and distinctly heart-shaped. The leaf apex is elongated into a slender "drip tip". 12 |
| Leaf Texture | Thinner, softer, and matte. The 'Micans' form is velvety. 13 |
| New Growth Mechanism | New leaves emerge from a cataphyll, a papery sheath that protects the developing leaf and later falls off. 4 |
| Petiole (Leaf Stalk) | Smooth and rounded where it connects to the vine. 3 |
| Aerial Roots | Produces multiple thin, wiry aerial roots at each node. 4 |
| New Leaf Color | New leaves on the standard green variety often have a brownish or coppery-pink tint before turning green. 12 |
These physical traits are the result of different evolutionary adaptations. The cataphyll is a modified leaf that shields new growth, a structure found in many philodendrons. 12 The pronounced drip tip helps channel water off the leaf surface in wet tropical habitats, preventing fungal growth. 13 Understanding these functional differences aids in identification.
Section 4: Growth Habit and Morphology
The Heart-Leaf Philodendron is a hemiepiphyte, meaning it can grow on the forest floor before climbing a tree, or it can start its life as an epiphyte in a tree's branches. 8, 16 This climbing ability is key to its development. The plant exhibits ontogeny, meaning it has physically distinct juvenile and adult forms. 8

Juvenile Form
This is the common form sold as a houseplant, characterized by:
- Small Leaves: Heart-shaped leaves are typically 2 to 4 inches (5 to 10 cm) long. 1
- Trailing Habit: Vines have long internodes (the space between leaves) and are thin and flexible, ideal for hanging baskets. 9
- Limited Climbing: Aerial roots are small and used for minor anchoring.
Mature Form
When given a support to climb, P. hederaceum can transition to its adult form. 8 The mature form features:
- Large Leaves: Leaves can grow to 12 inches (30 cm) or more in length. 1
- Robust Stems: Internodes shorten and stems become thicker and more rigid to support the plant's weight. 22
- Flowering Potential: Only the mature form can produce an inflorescence (a spathe and spadix), though this is rare indoors. 1
This transformation is triggered by environmental cues, primarily physical contact with a support surface. As the plant climbs, it mimics its natural ascent toward the brighter light of a forest canopy. 17 This triggers a hormonal shift, causing the plant to invest energy in larger leaves for more efficient photosynthesis and stronger stems for stability. 21, 22 Studies confirm that mature leaves develop a higher stomatal density to better capture light. 22 Therefore, providing a climbing structure is the primary method for encouraging the plant to develop its larger, mature form.
Section 5: Popular Cultivars
The species' genetic diversity has led to several popular cultivars and sports (spontaneous genetic mutations). 23 These variations offer different colors and textures.

'Brasil'
The most common variegated cultivar.
- Appearance: Each dark green leaf has a central splash of chartreuse, lime green, or yellow variegation. The pattern varies between leaves. 24
- Care Nuances: To maintain bright variegation, provide consistent bright, indirect light. In lower light, the variegation may fade. 26
'Micans'
Valued for its unique texture and color.
- Appearance: The juvenile leaves have a velvety texture. The color is an iridescent mix of deep green and coppery-red, shifting with the light. 10 The undersides are often a purplish-red.
- Care Nuances: This is a form of P. hederaceum var. hederaceum . 10 Its coloring is light-dependent; brighter, indirect light enhances the red and bronze tones. 10
'Lemon Lime'
Also sold as 'Neon', this cultivar has bright, uniformly colored leaves.
- Appearance: Leaves are a vibrant chartreuse or neon green. 29 New leaves may emerge with a pinkish-yellow hue. 31
- Care Nuances: Requires bright, indirect light to maintain its color. Insufficient light will cause the leaves to fade to a duller green and the plant to become leggy. 29
'Variegata'
The classic white-variegated form.
- Appearance: Displays irregular splashes and sectors of creamy white on the green leaf surface. 33 The pattern is unstable and varies widely from leaf to leaf. 36
Advanced Sports: 'Rio', 'Gabby', and 'Silver Stripe'
For collectors, several specific sports have been isolated for their unique variegation patterns. 23
- 'Silver Stripe': A cream or light green center is bordered by a silver stripe, which is then bordered by the dark green leaf margin. 23
- 'Rio': A stable sport with a silvery center stripe, followed by a layer of cream, another layer of silver, and a dark green leaf edge. 23
- 'Gabby': A highly unstable sport prized for large sections of pure cream. These leaves lack chlorophyll and are delicate, requiring optimal conditions. 23
Variegation with white or cream results from a mutation where some tissues lack chlorophyll, the pigment for photosynthesis. These non-green sections cannot produce energy. Therefore, providing variegated plants with more light is a requirement for survival. 27 Bright, indirect light ensures the green parts of the leaves can produce enough energy to support the entire plant. In low light, the plant may revert by producing all-green leaves to create more energy, causing the variegation to disappear. 36
Section 6: Care Instructions
Philodendron hederaceum is a tolerant houseplant, but it grows best when its native tropical conditions are replicated.
Light
Proper light is critical for plant health.
- Ideal Conditions: Thrives in sustained, bright, indirect light, which mimics dappled sunlight on a forest floor. 1 Variegated cultivars require this light level to maintain their color. 27
- Scientific Measurement: The optimal range for vigorous growth is a Photosynthetic Photon Flux Density (PPFD) of 50-250 µmol/m²/s , 40 equivalent to 200-400 foot-candles (FC) or 2,000-4,000 lux . 40
- Signs of Too Little Light: Slow growth, leggy stems (long spaces between leaves), and fading variegation. 43
- Signs of Too Much Light: Scorched leaves with pale, yellow, or brown patches and crispy edges from direct sun. 2
- Practical Placement: Place near an east-facing window or a few feet from a south- or west-facing window. A sheer curtain can be used to diffuse direct light. 27
Watering
Incorrect watering is a common cause of problems.
- Method: Use the "drench and dry" method. Water thoroughly until it flows from the drainage holes, then discard excess water from the saucer. Do not water again until the top 1-2 inches (2.5-5 cm) of soil are dry. 2
- Signs of Overwatering: Yellowing lower leaves, soft or mushy stems at the base, and root rot. 27
- Signs of Underwatering: Limp, drooping leaves, brown and crispy leaf edges, and stunted growth. 26
Soil and Substrate
As a hemiepiphyte, this plant needs a potting mix with good moisture retention and aeration.
- Core Principle: The soil mix must prevent waterlogging and allow oxygen to reach the roots. Heavy soil will lead to root rot. 25
- Ideal DIY Aroid Mix: Combine equal parts standard potting mix, orchid bark (for structure), and perlite (for drainage). 26 Amendments like coco coir (moisture retention) or horticultural charcoal (absorbs impurities) can also be added. 51
- Soil pH: Prefers a slightly acidic pH range of 5.5 to 6.5 . 40 Most peat-based mixes are within this range.
Temperature and Humidity
These plants are native to warm, humid regions.
- Temperature: The ideal range is 65-85°F (18-29°C) . 24 Temperatures below 55°F (13°C) can cause damage. Keep plants away from cold drafts. 26
- Humidity: While tolerant of average household humidity (~40%), the plant will grow more robustly in higher humidity. 27 Aim for 50-70% . 10 Increase humidity by grouping plants, using a pebble tray, or running a room humidifier. 29
Fertilizer
Supplemental nutrients are beneficial during the growing season.
- Type and Strength: Use a balanced, water-soluble liquid fertilizer (e.g., 10-10-10 NPK ratio), diluted to half the recommended strength to avoid root burn. 31, 48
- Frequency: Feed every 4-6 weeks during the spring and summer growing season. 48
- Dormancy: Stop fertilizing in fall and winter when growth slows. Fertilizing a dormant plant can cause mineral salt buildup and root damage. 26
Pruning and Shaping
Pruning maintains the plant's health and appearance.
- Purpose: Trimming controls vine length, encourages fuller growth, and removes dead leaves. 1 Unpruned vines can become sparse and leggy. 32
- Technique: To promote branching, use clean scissors to snip a vine just above a leaf node. The plant will typically send out new shoots from that node, creating a denser plant. 55 The cuttings can be used for propagation.
Section 7: Propagation Methods
Philodendron hederaceum is easy to propagate, especially during the spring and summer growing season. 58 All methods require a node —the bump on the stem where new leaves and roots emerge. A cutting must have at least one node to grow.
Step 1: Taking the Cutting
Using clean, sharp scissors, cut a 4-6 inch (10-15 cm) segment of a healthy vine that includes at least two nodes.28 Remove the leaf from the lowest node; this node will be placed in the rooting medium. Applying a rooting hormone is optional and not typically necessary for this plant. 19
Expected Timeline: Root development usually begins within 2 to 4 weeks in good conditions. 26

Comparative Analysis of Propagation Media
Method 1: Propagation in Water
- Process: Place the cutting in a jar of room-temperature water, submerging the leafless node(s) but keeping the remaining leaves out of the water. 19 Place the jar in bright, indirect light and change the water every few days to keep it oxygenated. 19
- Pros: Allows you to watch the roots grow. 63
- Cons & Solution: Water-grown roots are fragile and can experience shock when moved to soil. To ease the transition, you can slowly add small amounts of soil to the water over a week before potting.
- When to Plant: When new roots are 1-2 inches (2.5-5 cm) long, plant the cutting in a suitable aroid mix. 26
Method 2: Propagation in Sphagnum Moss
This method balances moisture and air, mimicking natural rooting conditions.
- Process: Soak sphagnum moss in water, then squeeze it out until damp but not dripping. Pack the moss loosely in a small pot and place the node of the cutting into the moss. 63
- Pros: Promotes strong roots that transition well to soil, reducing transplant shock. 63
- Cons: The moss must be kept consistently moist but not waterlogged to prevent the stem from rotting or the new roots from drying out.
Method 3: Propagation Directly in Soil
This is the most direct method.
- Process: Fill a small pot with a moist, well-draining aroid mix. Plant the cutting directly into the soil, burying at least one node. 19 Firm the soil around the stem.
- Pros: Eliminates the transplanting step. The roots that form are already adapted to soil, preventing transplant shock. 63
- Cons: Root growth is not visible. The soil must be kept lightly and consistently moist, which can be difficult to balance.
Section 8: Critical Safety Warning: Toxicity Explained
Owners must be aware of this plant's toxic properties, especially in households with pets or small children.
WARNING: Philodendron hederaceum is toxic to cats, dogs, and humans if ingested. 6
The Toxin and Its Mechanism
All parts of the plant contain microscopic, needle-shaped crystals of insoluble calcium oxalate . 6 These crystals are called raphides . 67
Raphides are a defense mechanism. When the plant is chewed, these sharp crystals are released and pierce the soft tissues of the mouth, tongue, and throat, causing immediate pain and irritation. 67
Symptoms of Ingestion in Pets
According to the ASPCA and Pet Poison Helpline, symptoms of ingestion in cats and dogs include: 6
- Intense oral irritation, pain, and burning
- Swelling of the mouth, tongue, and lips
- Excessive drooling
- Pawing at the face
- Vomiting
- Difficulty swallowing
In rare cases, swelling of the upper airway can cause difficulty breathing. 65 If you suspect your pet has ingested philodendron, contact your veterinarian or an animal poison control center immediately.
Safety Measures for Your Home

- Keep Out of Reach: Place the plant where it is inaccessible to pets and children. Hanging baskets or high shelves are good options. 2
- Handle with Care: The plant's sap can cause mild skin irritation in sensitive individuals. Consider wearing gloves when pruning. 24
Section 9: Troubleshooting: A Diagnostic Guide
This guide helps identify and solve common problems with your Philodendron hederaceum .
| Common Problems, Causes, and Solutions | ||
|---|---|---|
| Symptom | Possible Causes | Solutions |
| Yellow Leaves |
1. Overwatering (Most Common)
45
2. Nutrient Deficiency 44 3. Natural Aging (Oldest leaves) 71 4. Too Much Light 71 |
1. Reduce watering; allow top 1-2 inches of soil to dry out.
2. Fertilize with a half-strength balanced liquid fertilizer or repot. 3. Remove the old leaf; this is normal. 4. Move the plant to a spot with bright, indirect light. |
| Brown, Crispy Tips or Edges |
1. Low Humidity
29
2. Underwatering 44 3. Fertilizer Burn (salt buildup) 45 |
1. Increase humidity by misting, using a pebble tray, or a humidifier.
2. Water thoroughly when the top layer of soil is dry. 3. Flush the soil with water to wash out excess salts. Reduce fertilizer use. |
| Leggy Growth (Long Stems, Few Leaves) | Insufficient Light 32 | Move the plant to a brighter location. Prune leggy vines just above a node to encourage bushier growth. |
| Small New Leaves |
1. Insufficient Light
73
2. Lack of Climbing Support 21 3. Needs Repotting (root-bound) |
1. Move to a brighter location.
2. Provide a moss pole or trellis to encourage climbing and mature leaf growth. 3. If root-bound, repot into a container 1-2 inches larger in diameter. |
| Pests (Spider Mites, Mealybugs, etc.) | Infestation. Pests feed on the plant. Fungus gnats indicate overly moist soil. 74 | Isolate the plant. Wipe off pests with rubbing alcohol or spray with insecticidal soap or neem oil. For fungus gnats, let soil dry out and use sticky traps. 76 |
| Disease (Root Rot) | Overwatering and Poor Drainage 45 | Prevention: Use well-draining soil and a pot with drainage. Treatment: Remove plant, trim any black/mushy roots, and repot in fresh, mostly dry soil. Water sparingly until it recovers. |
Section 10: Advanced Cultivation Techniques
Biophilic Design and Wellness
The popularity of P. hederaceum is an example of biophilic design, the concept that humans are drawn to nature. Studies suggest that incorporating plants into indoor spaces can reduce stress and improve mood. 77
The NASA Clean Air Study in Context
A 1989 NASA study found that houseplants, including Philodendron species, could remove volatile organic compounds (VOCs) like formaldehyde from the air in a small, sealed chamber. 78, 79
However, these lab conditions do not reflect a typical home or office, which has a much larger air volume and regular ventilation. 77 Subsequent analysis concluded that an impractical number of plants would be needed to significantly purify the air in a real-world setting. 77
While your Heart-Leaf Philodendron has a minor positive effect on air quality, its primary benefits are aesthetic and psychological. For significant air purification, proper ventilation and air purifiers are more effective.
Advanced Techniques
Using a Moss Pole
Encouraging P. hederaceum to climb is the key to developing its mature form.
- The Principle: The goal is for the plant's aerial roots to grow into the pole, not just be tied to it. 81 A moist sphagnum moss pole provides stability and a secondary source of moisture.
- Training: When repotting, insert the pole into the pot. Secure the vine against the pole, pressing the nodes into the moss. Keep the pole moist by misting it or pouring water down the top. As the roots anchor into the moss, the plant will produce progressively larger leaves. 82
Semi-Hydroponic Cultivation (LECA)
Growing P. hederaceum in a soilless medium like LECA (Lightweight Expanded Clay Aggregate) is an alternative to soil.
- The Principle: Semi-hydroponics uses an inert medium that wicks a nutrient solution to the roots from a reservoir. 40 This method provides constant water and nutrients and eliminates soil-borne pests.
- Transition: Philodendron species adapt well to this method. 84 To transition a plant, thoroughly wash all soil from its roots. Place the clean-rooted plant in a semi-hydroponic pot and surround it with LECA.
- Care: Maintain a water reservoir at the bottom of the pot and add a hydroponic fertilizer to the water. 84
Section 11: Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Quick answers to common questions about the Heart-Leaf Philodendron.
-
Why are my philodendron's leaves turning yellow?
The most common cause is overwatering. It can also be from nutrient deficiency, natural aging of lower leaves, or too much direct sun. Check soil moisture first.45 -
Can I grow a Heart-Leaf Philodendron in low light?
Yes, it tolerates low light, but growth will be slow and stems may become leggy.2 -
How fast does a Heart-Leaf Philodendron grow?
In ideal conditions (bright, indirect light and consistent care), it is a fast grower. Vines can reach lengths of 10 feet (3 m) or more.3 -
Is the Heart-Leaf Philodendron toxic to cats?
Yes, it is toxic to cats, dogs, and humans if ingested. It contains insoluble calcium oxalate crystals that cause oral irritation and pain.6 -
How do I make my variegated philodendron more variegated?
Provide more bright, indirect light. In low light, the plant may produce solid green leaves (reversion) to photosynthesize more effectively.27
Sources
Works cited
- Philodendron hederaceum - Plant Finder - Missouri Botanical Garden, https://www.missouribotanicalgarden.org/PlantFinder/PlantFinderDetails.aspx?kempercode=b611
- Heartleaf Philodendron - UF/IFAS Gardening Solutions, https://gardeningsolutions.ifas.ufl.edu/plants/houseplants/heartleaf-philodendron/
- Philodendron hederaceum (Heartleaf Philodendron, Parlor Ivy ..., https://plants.ces.ncsu.edu/plants/philodendron-hederaceum/
- Popular houseplants: Is it philodendron or pothos? | ILRiverHort | Illinois Extension | UIUC, https://extension.illinois.edu/blogs/ilriverhort/2020-12-17-popular-houseplants-it-philodendron-or-pothos
- Why Philodendron hederaceum is the correct name for Philodendron micans & P. scandens | UBC Botanical Garden Forums, https://forums.botanicalgarden.ubc.ca/threads/why-philodendron-hederaceum-is-the-correct-name-for-philodendron-micans-p-scandens.39604/
- Heartleaf Philodendron | ASPCA, https://www.aspca.org/pet-care/animal-poison-control/toxic-and-non-toxic-plants/heartleaf-philodendron
- Philodendron hederaceum var. hederaceum | Plants of the World ..., https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:77170908-1
- Philodendron - Wikipedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Philodendron
- Philodendron hederaceum var. hederaceum (Heart Leaf or Velvet Leaf Philodendron) - The Belmont Rooster, https://thebelmontrooster.com/families-of-familiar-plants/araceae-family/philodendron-hederaceum-heart-leaf-or-velvet-leaf-philodendron/
- Philodendron Micans: Care and Growing Guide - The Spruce, https://www.thespruce.com/philodendron-micans-care-5201173
- Is there a fancy name for the “regular ol' green heart leaf” philo? : r/philodendron - Reddit, https://www.reddit.com/r/philodendron/comments/t5xclk/is_there_a_fancy_name_for_the_regular_ol_green/
- Know your plants: how to tell the difference between a philodendron and a pothos, https://www.stamenandstemblog.com/blog/pothos-vs-philodendron
- Epipremnum or Philodendron? - Plants are the Strangest People, https://plantsarethestrangestpeople.blogspot.com/2009/03/epipremnum-or-philodendron.html
- Pothos vs. Philodendron: 4 Tips for Differentiating the Plants - 2025 - MasterClass, https://www.masterclass.com/articles/pothos-vs-philodendron
- Question about new leaves : r/philodendron - Reddit, https://www.reddit.com/r/philodendron/comments/11xv2z0/question_about_new_leaves/
- Philodendron hederaceum var. hederaceum | Colombian Plants made accessible, https://colplanta.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:77170908-1/general-information
- Philodendron Care Guide - Estabrook's, https://www.estabrooksonline.com/advice/article.asp?id=1233
- Natural variation within Aroid and other plant species. Exotic Rainforest rare tropical plants, https://www.exoticrainforest.com/Natural%20variation%20within%20aroid%20and%20%20plant%20species.html
- How To Grow And Care For Philodendron Outdoors - Southern Living, https://www.southernliving.com/philodendron-7373966
- FPS472/FP472: Philodendron scandens Heart Leaf Philodendron - University of Florida, https://edis.ifas.ufl.edu/publication/FP472
- Climbing Plants Like to Climb - Laidback Gardener, https://laidbackgardener.blog/2017/01/31/climbing-plants-like-to-climb/
- Does the same morphology mean the same physiology? Morphophysiological adjustments of Philodendron hederaceum (Jacq.) Schott, an isomorphic aroid, to ground-canopy transition | Request PDF - ResearchGate, https://www.researchgate.net/publication/325228475_Does_the_same_morphology_mean_the_same_physiology_Morphophysiological_adjustments_of_Philodendron_hederaceum_Jacq_Schott_an_isomorphic_aroid_to_ground-canopy_transition
- Philodendron hederaceum – Identifying Sports - Gabriella Plants, https://www.gabriellaplants.com/pages/philodendron-hederaceum-identifying-sports
- Philodendron | North Carolina Extension Gardener Plant Toolbox, https://plants.ces.ncsu.edu/plants/philodendron/
- Philodendron Brasil Plant Care Guide - Plantly, https://plantly.io/plant-care/philodendron-brasil/
- How to Grow and Care for Philodendron Brasil - The Spruce, https://www.thespruce.com/philodendron-brasil-care-guide-5204203
- How to Take Care of Philodendron | Plant Care and Tips - JOMO Studio, https://jomostudio.com/blogs/plant-with-jomo/how-to-take-care-of-your-philodendron
- Philodendron hederaceum - l'application Monstera, https://www.monstera-app.com/en/plants/varieties/philodendron-hederaceum-01GS5VPJKPZQR26ESJZNKEAABM
- Philodendron Lemon Lime Care Guide - Neon Heart Leaf Plant, https://youshouldplant.com/neon-philodendron-lemon-lime-care/
- Philodendron hederaceum 'Lemon Lime' - Fantastic Gardens, https://fantasticgardensofli.com/products/philodendron-hederaceum-lemon-lime
- Lemon Lime Philodendron | Philodendron Plants for Sale | Lively Root, https://www.livelyroot.com/products/philodendron-lemon-lime
- Philodendron | Lemon Lime | Care Difficulty - Easy | AmieSue.com - Nouveau Raw, https://nouveauraw.com/indoor-plants/varieties/philodendron-lemon-lime/
- Philodendron Hederaceum Variegata Plant in 2.5×3″ Deep Pot, https://kensphilodendrons.com/product/philodendron-hederaceum-variegata-plant-in-2x3-deep-pot/
- 4" Variegated Philodendron Hederaceum - BWH Plant Co, https://bwhplantco.com/products/4-variegated-philodendron-hederaceum
- Philodendron hederaceum variegata - Steve's Leaves, https://stevesleaves.com/products/philodendron-hederaceum-variegata
- Philodendron Hederaceum Variegata | 6" Pot - Plant Hawaii, https://planthawaii.com/product/philodendron-hederaceum-variegata-6-pot/
- Buy Philodendron hederaceum var. oxycardium variegata - Foliage Factory, https://www.foliage-factory.com/philodendron-hederaceum-var-oxycardium-variegata
- How to Grow and Care for Philodendron Rio - The Spruce, https://www.thespruce.com/philodendron-rio-growing-guide-5235405
- Growers Guide to Variegated Heart Leaf Philodendrons – PlantyTown, https://planty.town/blogs/plant-care/growers-guide-to-variegated-heart-leaf-philodendrons
- The Complete Philodendron Plant Care Guide - leafnjoy.com, https://leafnjoy.com/philodendron-plant-care/
- Light Requirements for Plants: Find Your Plant's PPFD and DLI | Photone - Grow Light Meter, https://growlightmeter.com/light-requirements-for-plants/
- Bright Indirect Light “Requirements” by Plant Type - House Plant Journal, https://www.houseplantjournal.com/bright-indirect-light-requirements-by-plant/
- Heartleaf Philodendron Plant Care Guide - Soltech, https://soltech.com/products/heartleaf-philodendron-care
- Heartleaf Philodendron Care Instructions - Plantify, https://plantify.co.za/pages/heartleaf-philodendron-care-instructions
- Troubleshooting Philodendron Leaves Turning Yellow or Brown, https://www.livelyroot.com/blogs/plant-care/philodendron-leaves-turning-yellow-or-brown
- How to Grow and Care for Heart-Leaf Philodendron - The Spruce, https://www.thespruce.com/heartleaf-philodendron-guide-5181702
- Philodendron Plant Care Tips! | Philodendron Problems: Yellowing & Browning Leaves! | - YouTube, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-ZUnPtovKus
- Heartleaf Philodendron Plant Care Guide - Healthy Houseplants, https://www.healthyhouseplants.com/indoor-houseplants/heartleaf-philodendron-plant-care-guide/
- Soil Composition: what works best for you? : r/philodendron - Reddit, https://www.reddit.com/r/philodendron/comments/s12ul1/soil_composition_what_works_best_for_you/
- Philodendron: A Basic Care Guide - Reddit, https://www.reddit.com/r/philodendron/comments/1j0lkij/philodendron_a_basic_care_guide/
- My DIY Aroid Soil Mix Recipe - Hoya Treasures, https://hoyatreasures.com/blogs/houseplant-care/my-diy-aroid-soil-mix-recipe
- The Best Soil for Philodendrons: A Comprehensive Guide, https://xanhxanhurbanforest.com/the-best-soil-for-philodendrons/
- Heartleaf Philodendron Plant Care Guide - Healthy Houseplants, https://www.healthyhouseplants.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/healthyhouseplants_com_indoor_houseplants_heartleaf_philodendron_plant_care_guide.pdf
- How to care for the Heartleaf Philodendron | Plants 101 - The Sill, https://www.thesill.com/blogs/plants-101/how-to-care-for-philodendron
- Some philodendron pruning questions : r/IndoorGarden - Reddit, https://www.reddit.com/r/IndoorGarden/comments/6oj0uy/some_philodendron_pruning_questions/
- www.picturethisai.com, https://www.picturethisai.com/care/pruning/Philodendron_hederaceum.html#:~:text=Prune%20the%20old%20growth%20to,new%20growth%20in%20heartleaf%20philodendron.
- How to Prune Heartleaf philodendron - PictureThis, https://www.picturethisai.com/care/pruning/Philodendron_hederaceum.html
- How to propagate Philodendron - Plants For All Seasons, https://www.plantsforallseasons.co.uk/blogs/philodendron-care/how-to-propagate-philodendron
- How to Propagate a Philodendron 2 Ways - The Spruce, https://www.thespruce.com/philodendron-propagation-7113317
- Philodendron hederaceum Propagation: Tips for Successful Growth - Aquarius Mediaa, https://aquariusmediaa.com/philodendron-hederaceum/
- Learn How to Propagate Philodendron with This Simple Guide, https://www.livelyroot.com/blogs/plant-care/how-to-propagate-philodendron
- How to Propagate Philodendron: Step-by-Step Water & Soil Guide - Plant Vault, https://www.plantvault.com/blogs/propagation/how-to-propagate-philodendron
- Is it better to propagate a Philodendron in water or soil? - Reddit, https://www.reddit.com/r/philodendron/comments/ps32g3/is_it_better_to_propagate_a_philodendron_in_water/
- Philodendron - Highland Moss, https://highlandmoss.com/portfolio/philodendron/
- Philodendron Are Toxic To Pets | Pet Poison Helpline®, https://www.petpoisonhelpline.com/poison/philodendron/
- Philodendron Poisoning in Chickens, https://chickendvm.com/poisonous/philodendron
- Split Leaf Philodendron Poisoning in Dogs - Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, Recovery, Management, Cost - Wag!, https://wagwalking.com/condition/split-leaf-philodendron-poisoning
- Raphide - Wikipedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Raphide
- Variegated Philodendron Poisoning in Dogs - Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, Recovery, Management, Cost - Wag!, https://wagwalking.com/condition/variegated-philodendron-poisoning
- Philodendron hederaceum var oxycardium All Zones - UF/IFAS Assessment, https://assessment.ifas.ufl.edu/site/assets/files/4432/philodendron_hederaceum_var_oxycardium_wra2015.pdf
- Philodendron Turning Yellow? 7 Causes and How to Fix - The Spruce, https://www.thespruce.com/why-is-my-philodendron-turning-yellow-8705503
- Why are the leaves on my Philodendron turning yellow? - Bloomscape, https://bloomscape.com/common-issue/why-are-the-leaves-on-my-philodendron-turning-yellow/
- Comparison of a Philodendron hederaceum (Heartleaf) and a Epipremnum aureum (pothos). They are both beautiful plants. But my favorite is the pothos. Why? The Texture. I absolutely love the texture of the pothos! All varieties. - Reddit, https://www.reddit.com/r/pothos/comments/khtu62/comparison_of_a_philodendron_hederaceum_heartleaf/
- Common Diseases of Heartleaf Philodendron: A Comprehensive Guide - Cafe Planta, https://cafeplanta.com/a/blog/common-diseases-of-heartleaf-philodendron-a-comprehensive-guide
- 5 Philodendron Pests: How to ID and Eradicate Them - Epic Gardening, https://www.epicgardening.com/philodendron-pests/
- Common Heartleaf Philodendron Pests (And What To Do About ..., https://cafeplanta.com/blogs/resources/heartleaf-philodendron-pests
- Debunking NASA study on air-cleaning plants - Garden Bite, https://gardenbite.com/debunking-nasa-study-on-air-cleaning-plants/
- NASA Clean Air Study - Wikipedia, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/NASA_Clean_Air_Study
- Houseplants, Indoor Air Pollutants, and Allergic Reactions - NASA ..., https://ntrs.nasa.gov/citations/19930072972
- 50 Best Air Purifying Plants | Our Houseplants, https://www.ourhouseplants.com/guides/50-plants-that-clean-the-air
- Moss Poles, Trellises, and Climbing Houseplants - City Floral Garden Center - Denver Colorado, https://cityfloralgreenhouse.com/2023/01/moss-poles-trellises-and-climbing-houseplants/
- DIY Moss Pole for Indoor Plants in 4 Easy Steps - Swansons Nursery, https://www.swansonsnursery.com/blog/diy-moss-pole-for-indoor-plants-four-easy-steps
- Grow Large Leaves Philodendron | A Comprehensive Guide on How to Use Moss Pole For Aroid - YouTube, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yjegcYPK9Wc
- Complete Guide to Growing Philodendrons in LECA & Pon - Semi Hydro, https://semi-hydro.com/philodendrons/
- Growing Philodendrons in Semi-Hydroponics - LECA Addict, https://www.lecaaddict.com/plants-in-leca/philodendron